Aiseesoft FoneTrans is an easy-to-use iOS data transfer tool for syncing your iPhone, iPad, or…
What is Rotating Wi-Fi Address and How to Enable it on iPhone Running iOS 18
Starting with iOS 18, iPadOS 18, and macOS Sequoia, Apple enhanced the Private Wi-Fi Address feature, now known as ‘Rotate Wi-Fi Address.’ This feature protects your privacy by preventing people from tracking you. In this article, let’s learn what is Rotating Wi-Fi Address and how to enable it on your iPhone running iOS 18 and up.

Table of Contents
What is Rotating Wi-Fi Address on iOS 18?
Rotating Wi-Fi Address is an enhanced version of the Private Wi-Fi Address feature, introduced in iOS 14. The Private Wi-Fi Address is similar to the Random MAC Address feature on Android and Windows. When enabled, your iPhone generates a new random MAC address for each wireless network it connects to, creating what are known as private addresses.
The new Rotating Wi-Fi Address in iOS 18/iPadOS 18 and macOS Sequoia differs from the Private Wi-Fi Address. The new feature randomly changes your device’s Wi-Fi address, making it difficult to track using a MAC address. Tracking can occur when your consistent address is visible to other devices and people on the same network, but Rotating Wi-Fi Address prevent this.
How to Enable Rotating Wi-Fi Address on iPhone Running iOS 18?
In older iOS builds, the Private Wi-Fi address feature was enabled by default, whereas the Rotate Wi-Fi address requires manual activation on iOS 18. Here is how to do it.
1. First, open the Settings app on your iPhone and select the Wi-Fi option.
2. Next, tap the (i) icon next to the Wi-Fi network you’re connected to.
3. Scroll down and toggle on the “Rotate Wi-Fi address” feature.
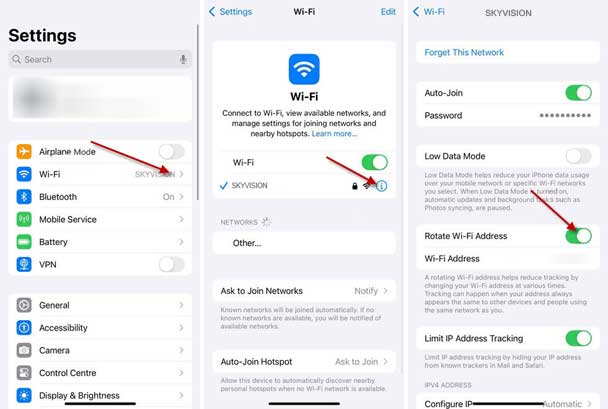
4. Repeat these steps for each network on your iPhone.
Important: Keep in mind that if you are connecting to a network that relies on MAC addresses for authentication, the Rotating Wi-Fi Address may cause connection issues. In such cases, you should disable this feature on your device.
Pros and Cons of Using a Private and Rotating Wi-Fi Address
Using a Private or Rotating Wi-Fi address can protect your privacy. This feature can block tracking of your device and prevent operators from serving ads when you connect to a public network.
However, using a Private or Rotating Wi-Fi address can also cause issues when using networks protected with MAC address filtering. This is because it complicates the identification of trusted devices.
Note: This article was first published in August 2024 and updated in November 2024 with few changes.



